Technically, a hard disk should contain either as many as four primary partitions, or one to three primaries along with a single extended partition. Each of these partitions are described by a 16-byte entry in the Partition Table which is located in the Master Boot Record.
src: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Partition_(computing)
Many poeple confused with Linux partitioning system when they are installing Linux for the first time. In linux they see hda1 then hda5 but they are familiar with C:, D: etc
your HDD can be recognize by hda, hdb,hdc,hdd, sda, sdb etc depending on the master, slave and cable position. Here i am describing with hda

A HDD with 4 Primary Partitions
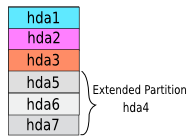
here hda4 is the full extended partion so extended partition start from hda5
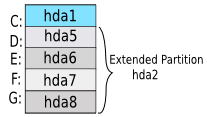
generally a windows / most of the PC has this type of partition system.
here hda2 is the full extended partion and hda3 and hda4 are reserved as we can create 2 more primary partitions so extended partition start from hda5
Extended partition generally start from hda5
so if anyone want to install linux in his G: drive then he need to delete the hda8 then create 2 partitions
one swap space (it can be compare with windows virtual memory) ram * 2 (size recomanded) and another root / partition.
Note: I would suggest to create swap first then root / partition and at the last of the HDD sector more then or at least 8 MB free unallocated space. When user need to reinstall windows sometimes it creates problem, if there is no free unallocated space.

 in pidgin
in pidgin