This is an example, how to start working on speech detection application for iPhone.
We have two major task:
1. Access the audio data.
2. Implement the logic part.
Task1: Access the audio data:
Download SpeakHere Example code from Apple:
http://developer.apple.com/iphone/library/samplecode/SpeakHere/index.html
Open “Classes->Play & Record->AQRecorder.mm” and edit the folloding function:
// AudioQueue callback function, called when an input buffers has been filled.
void AQRecorder::MyInputBufferHandler(...)
Add the following code to access the audio data:
//for signed 16-bit little-endian
SInt16 *buf = (SInt16 *)inBuffer->mAudioData;
for(int i=0; i< inBuffer->mAudioDataByteSize / 2; i=i+2) {
printf("n%dn%d ", buf[i], buf[i+1]);
}
(Please feel free to let me know if I am doing anything wrong…)
Run the application. You will get the raw data in gdb/console/log.
Copy the data in a text file and plot it.
Download gnuplot and AquaTerm
I have copied the data in a text file name “hello.txt” and saved it in my home directory.
Plot this, in gnuplot using the following command:
gnuplot>plot “hello.txt”
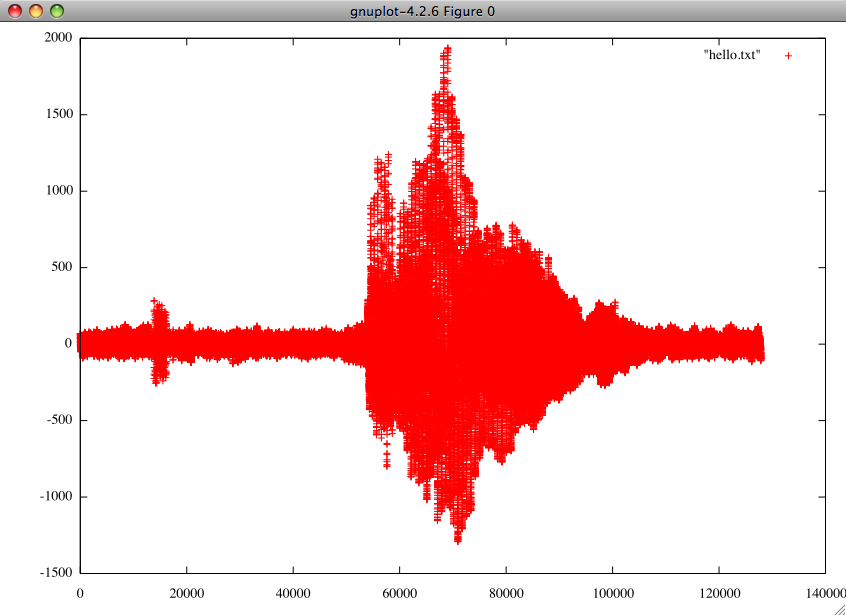
Task2: Implement the logic part:
For speech detection purpose we do not need to check all the data. Set some filter to check the data within some range. You can also try with the maximum and minimum value.
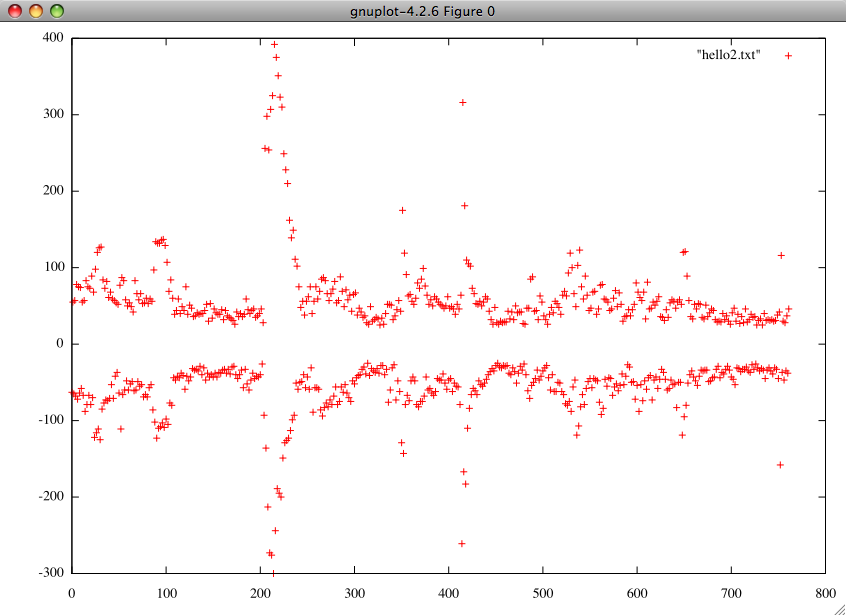
As the maximum and minumum value is similar, you can simply check one part.
If you want to detect specific type of speech or sound, analyze the graph by taking some sample.
Understand the logic and implement a coded logic to detect it.
For normal detection purpose take many sample and do R&D youself.
Please note that the mic “Input Volume” may affect your data.


